本周有两道图相关题目,可以复习一下图的最短路算法。
1.


直接实现即可。
class Solution:
def isCircularSentence(self, sentence: str) -> bool:
words = sentence.split()
return words[0][0] == words[-1][-1] and all(words[i][-1] == words[i + 1][0] for i in range(len(words) - 1))
2.

可以证明,如果合法的组对方式存在,最小数一定与最大数组对。否则,最大数跟任意其他数组成的数对之和,一定大于最小数与任意数组成的数对之和。然后,递归应用这一条推理,就能证明如果合法的组对方式存在,一定是第 i 小与第 i 大进行组队。之后实现就比较简单了。
class Solution:
def dividePlayers(self, skill: List[int]) -> int:
skill.sort()
prod = 0
total = skill[0] + skill[-1]
for i in range(len(skill) // 2):
if skill[i] + skill[- 1 - i] != total:
return -1
prod += skill[i] * skill[- 1 - i]
return prod
3.
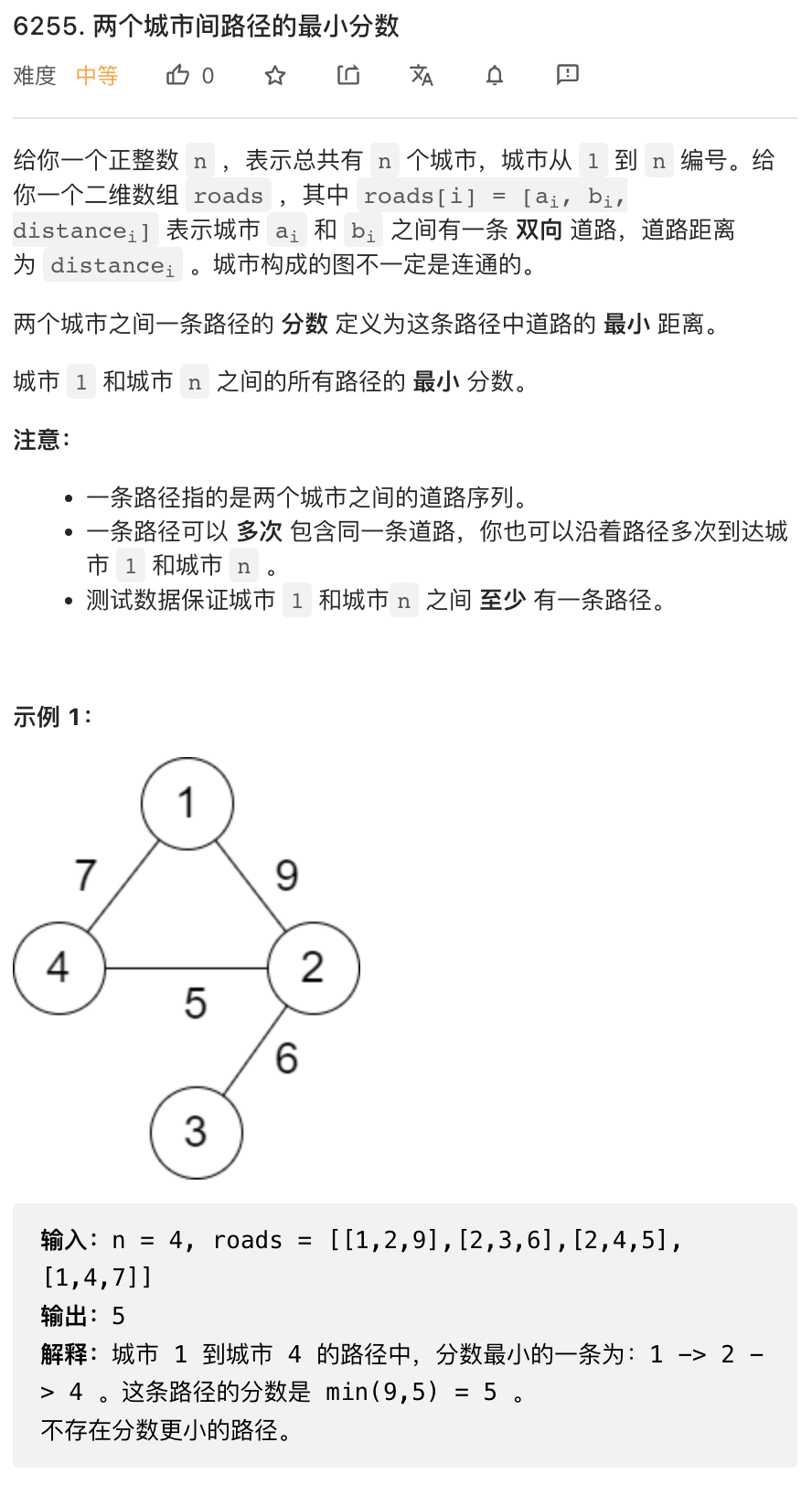
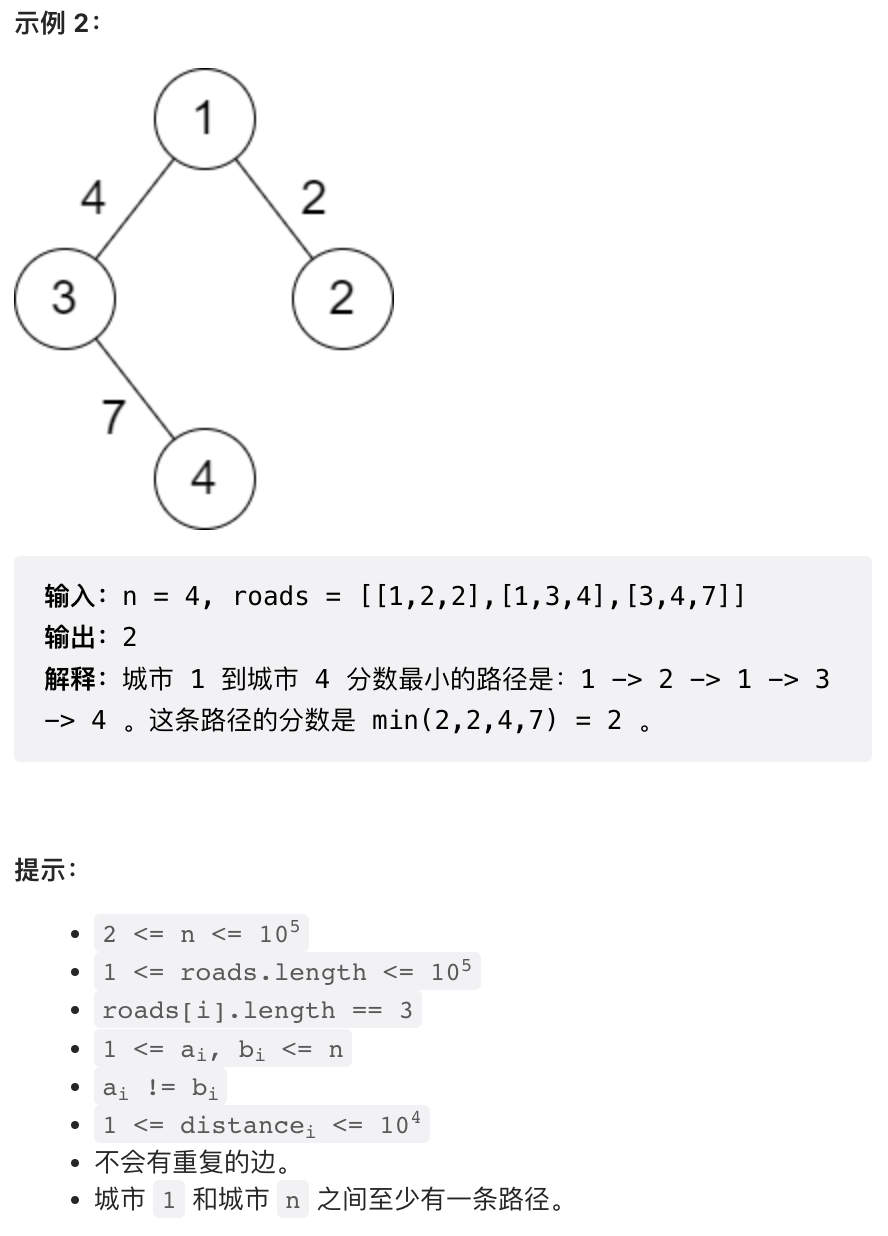
这个问题我觉得是本次周赛最有意思的问题。谈到最短路算法,我们当然会首先想到 dijkstra 算法。但这个问题中总路径长度定义比较特殊,是整条路径中最短的一条子路径的长度。这个定义其实类似于负权路径,所以不能使用 dijkstra 算法,而是要使用类似于 bellman ford 算法。
这两个算法尽在实际实现时区别很小,主要是 dijkstra 使用优先队列,bellman ford 使用队列。但 dijkstra 算法会保证每个节点只进队列一次,bellman ford 却不能保证。这一点是理论分析结果,在代码上是不会有体现的。bellman ford 使用优先队列也能运行,这个问题上,使用优先队列会更快的找到最短路径,从而更快收敛。
# 这看上去是个 dijkstra, 实际上是个 bellman ford
def shortest(graph, from_node):
import heapq
node_num = len(graph)
res = [float("inf")] * node_num
heap = []
# 队列中保存 (distance, node)
# 注意初试节点 distance 需要设置为一个大数
heapq.heappush(heap, (1e9, from_node))
while len(heap):
weight, node = heapq.heappop(heap)
if weight >= res[node]:
continue
res[node] = weight
for child in graph[node]:
# 这里与 dijkstra 唯一的不同是求和改成 min
heapq.heappush(heap, (min(weight, child[1]), child[0]))
return res
class Solution:
def minScore(self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]]) -> int:
graph = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)]
for x, y, d in roads:
graph[x].append((y, d))
graph[y].append((x, d))
return shortest(graph, 1)[n]
4.
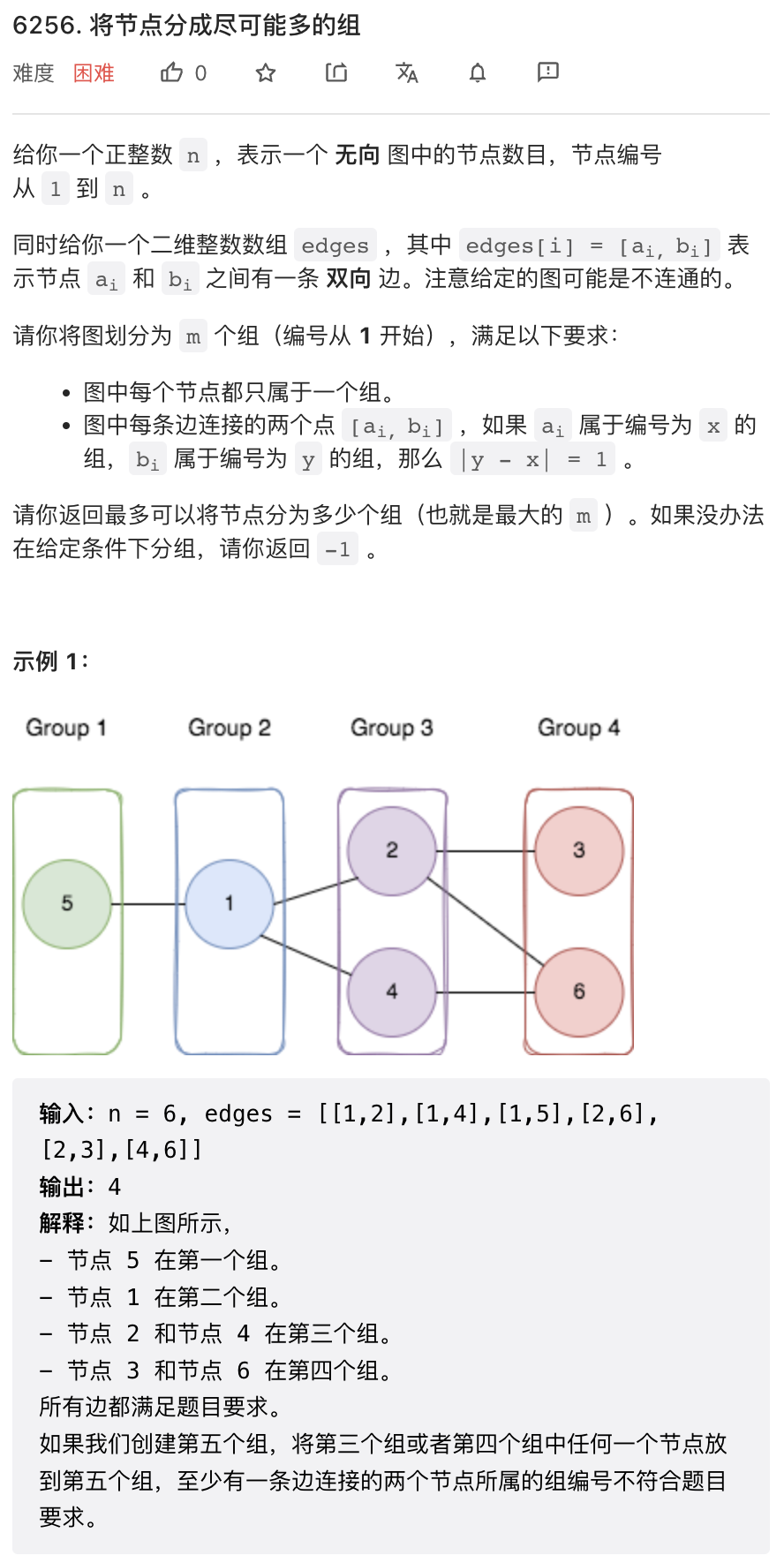

这个问题其实并不复杂,只是操作有点繁琐。
很容易想到一个思路:从某一点出发,然后进行类似于 BFS 的层次遍历,遍历过程中检查是否合法,然后遍历的最大层数即为所求。这个思路成立的前提是,存在一种最优划分方法,其第一组只有一个节点。这一点是可以证明的。如果第一组有一个以上节点,只需要任意保留一个节点,将其他节点划分到第三组,则也是一个合法的划分。于是,我们可以从每个节点出发,层次遍历检查。这样时间复杂度是 O(n * num_edges) 在这个问题上时间复杂度有点紧张,保险起见使用 C++ 实现。
然后,需要注意这个题不保证图是联通的。所以我们需要分别求解每个子图。所以我们还得进行一遍子图划分,子图划分最简单的方法是使用并查集。最终代码如下。
// 并查集模板
struct MergeFindSet {
std::vector<int> p;
MergeFindSet(int n) : p(n) { init(); }
int find(int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = find(p[x]); }
void merge(int root, int child) { p[find(child)] = find(root); }
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < int(p.size()); i++) p[i] = i;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int magnificentSets(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
// 构建图和并查集
vector<vector<int>> G(n + 1);
MergeFindSet mfs(n + 1);
for(auto& p: edges) {
G[p[0]].push_back(p[1]);
G[p[1]].push_back(p[0]);
mfs.merge(p[0], p[1]);
}
// 每个连通子图的最大划分
// 连通子图按照并查集集合需要划分,最大 n
// -2 代表这个序号没有对应的子图
// -1 代表这个子图无法分割
vector<int> subg(n + 1, -2);
// 尝试从每个节点出发进行层次遍历
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int ng = bfs(G, i);
// 按照子图在并查集中的序号更新结果
int sub = mfs.find(i);
subg[sub] = max(subg[sub], ng);
}
// 最终划分数量是所有子图划分数量之和
// 但如果任意子图无法划分,则无法划分
int res = 0;
for(int x: subg) {
if(x == -1) return -1;
if(x == -2) continue;
res += x;
}
return res;
}
// BFS 层次遍历
int bfs(vector<vector<int>>& G, int node) {
// 节点所属的 group
vector<int> group(G.size(), -1);
group[node] = 1;
queue<int> q;
q.push(node);
while(q.size()) {
int curr = q.front();
q.pop();
int cg = group[curr];
for(int child: G[curr]) {
int cc = group[child];
if(abs(cc - cg) == 1) continue;
// 如果发现一个近临节点的 group 序号差异不是 1 则划分失败
if(cc != -1) return -1;
// 标记新的近临界点 group 序号
group[child] = cg + 1;
q.push(child);
}
}
return *max_element(group.begin(), group.end());
}
};