| 中国站传送门 | 国际站传送门 |
双周赛笔记从简,有兴趣可以留言讨论。
1. 有效时间的数目
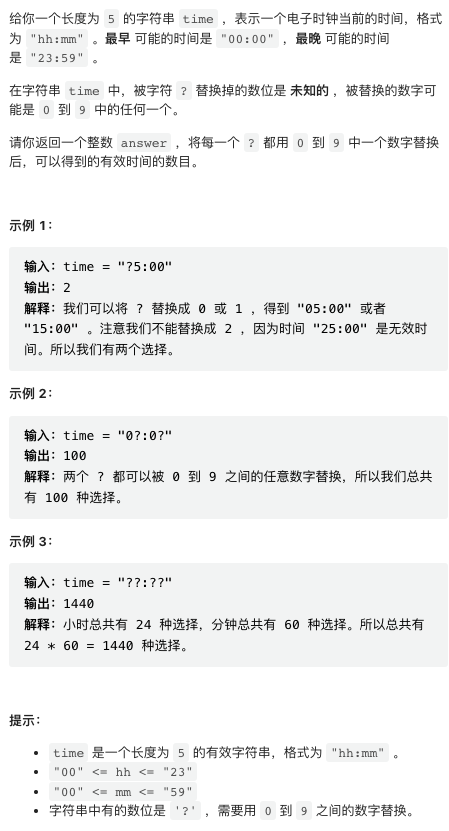
这种题目千万不要用花哨的方法,能暴力枚举就不要废话。
class Solution:
def countTime(self, s: str) -> int:
cnt = 0
for h in range(24):
for m in range(60):
t = "%02d:%02d" % (h, m)
match = True
for p, q in zip(s, t):
if p != q and p != '?':
match = False
break
cnt += 1 if match else 0
return cnt
2. 二的幂数组中查询范围内的乘积

看上去很难,实际上很简单。注意 powers 长度不会超过 所以暴力枚举即可。
class Solution:
def productQueries(self, n: int, queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
powers = []
curr = 1
while n:
if n & 1:
powers.append(curr)
curr <<= 1
n >>= 1
mod = 10 ** 9 + 7
res = []
for left, right in queries:
p = 1
for i in range(left, right + 1):
p = p * powers[i] % mod
res.append(p)
return res
3. 最小化数组中的最大值
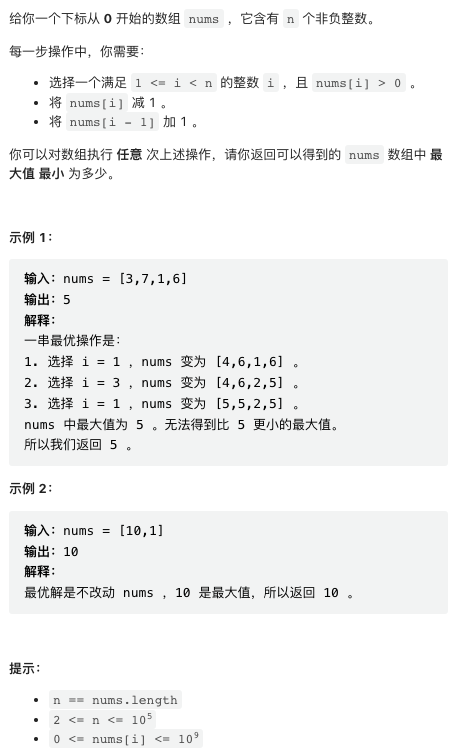
数学题。注意我们可以随意的把一个数的值移动到之前的数上,待求结果等于每个位置「前缀平均值向上取整」的最大值。
class Solution:
def minimizeArrayValue(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = prefix = 0
for i, x in enumerate(nums):
prefix += x
res = max(res, prefix // (i + 1) + (prefix % (i + 1) != 0))
return res
4. 创建价值相同的连通块
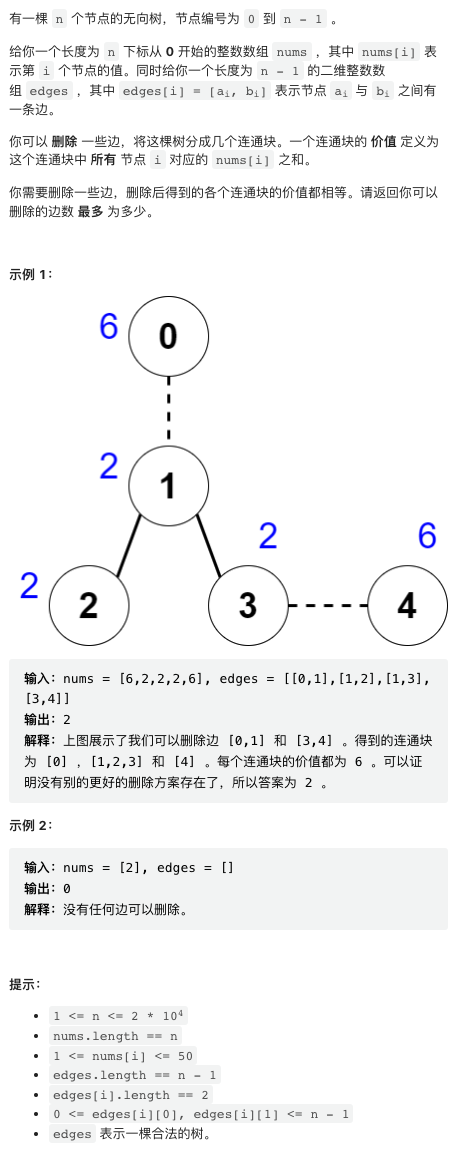
这个题目有点难度,比赛时差点翻车。
思路的突破点有两个。
其一是,这个问题属于检验比求解要简单的题目,也即我们先假设分割之后的每个子图和为 t, 检查给定 t 值的合法性要比求解 t 值容易。并且由于 t 必须是原图节点之和的因数,它的候选集不会太大。
其二是检验方法。考虑原图(实际上是一棵树)的一个叶节点,
- 如果其值大于 t, 则无法分割,t 不合法
- 如果其值等于 t, 则这个叶节点必须独立成一个子图,我们可以将其从图上删去
- 如果其值小于 t, 则必须将其与其父节点归为一个子图。方便起见,我们可以将其值加到父节点上,然后将其删去
由于原图是一棵树,我们可以反复执行这个操作,直到整个图全部删除,或者监测到某个节点无法分割。
class Solution {
public:
int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for(auto& p: edges) {
g[p[0]].push_back(p[1]);
g[p[1]].push_back(p[0]);
}
int total = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
int large = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int t = large; t <= total; t++) {
if(total % t == 0) {
if(dfs(g, nums, 0, -1, t) == 0) {
return total / t - 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& g, vector<int>& nums, int curr, int pre, int t) {
int total = nums[curr];
for(int child: g[curr]) {
if(child != pre) {
int r = dfs(g, nums, child, curr, t);
if(r == -1) return -1;
total += r;
}
}
return total > t ? -1 : (total == t ? 0 : total);
}
};